Common Categories of Playthings
-
According to Smilansky and Shefatya’s (1990) categories of play, there are four types of play, which include the following:
-
Constructive play, in which children build and make things;
-
Functional play, in which children manipulate toys; also called manipulative play;
-
Games with rules, in which children learn to understand the ideas of rules, accept the rules, and play by the rules; and
-
Dramatic/sociodramatic play, in which children pretend to be other people by using props; also called creative and imaginative play.
-
-
Also, there are cognitive play, exploratory play, and motor-training related activities.
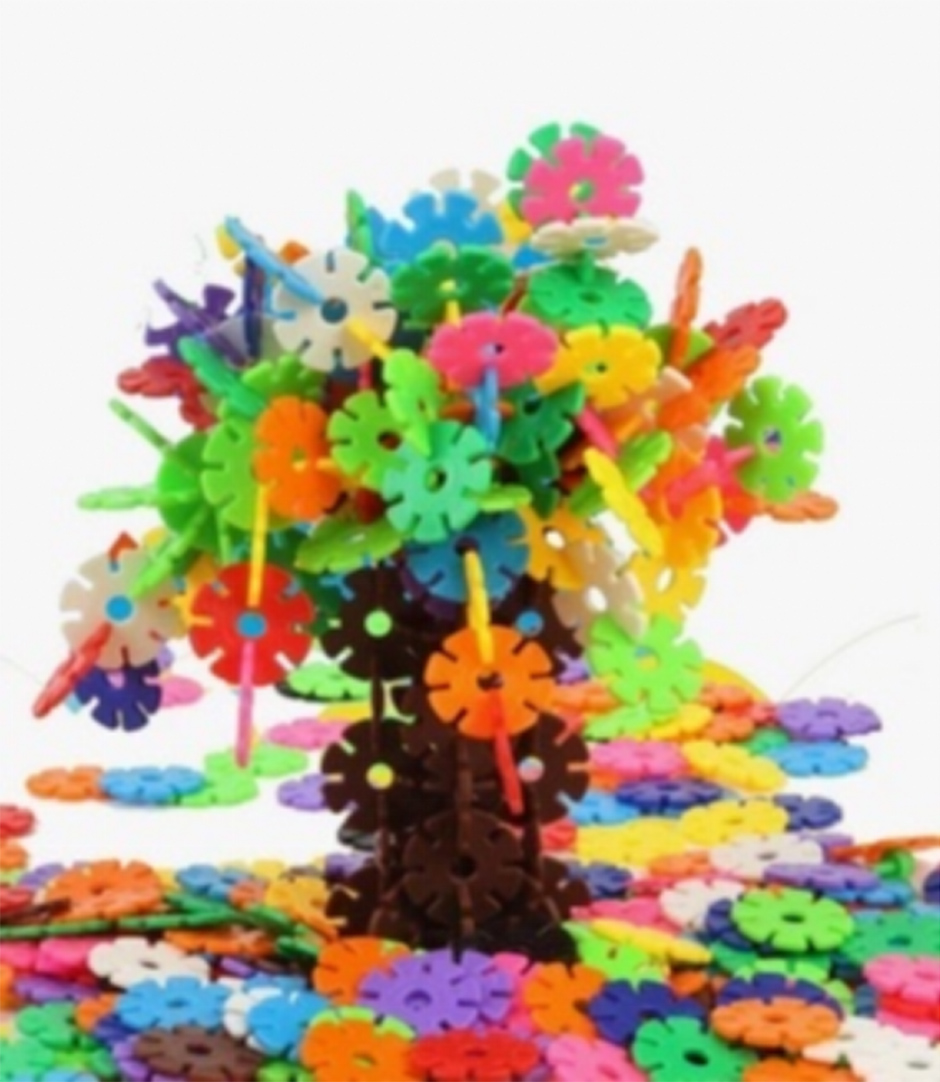
Constructive Play (建構性遊戲)
-
The constructive play materials are open-ended
-
Children use materials to creatively and intentionally build something
-
The materials take many forms, such as blocks, Legos, gears, playdough, sand, recycled materials, etc.






Cognitive Play (認知訓練遊戲)
-
The cognitive play materials build children’s problem-solving and other cognitive skills, such as sorting, categorizing, counting, matching, etc.
-
The materials include puzzles, matching games, constructing and building blocks, etc.


























Manipulative Play (操作性遊戲)
-
Children develop their fine motor skills through manipulating the materials to gain control over their movements and to coordinate physical actions
-
Through manipulating materials, children learn about:
-
The concepts of size, shape, weight, length, heights, cause and effect (e.g., object permanence box), sequencing, order, patterns, etc.
-
The skills of analysing and solving problems, etc.
-














Exploratory Play (探索性遊戲)
-
Children use all their senses to explore, for example children examine objects by looking, touching, listening and moving it to learn about how they can influence the world around them.
-
Materials include magnifying glass, magnets, specimens, etc.












Creative and Imaginative Play (創作及想像性遊戲)
-
Children use their imagination to learn and play with toys and props.
-
They use symbols (an object) to represent other objects. For example, the child uses a banana to stand for a phone.






Motor-training related Activities (體能訓練活動)
-
Through involving in the motor-training related activities, children involve in the use of motor (gross and fine motor) skills, including
-
Fine motor skills such as hand-eye coordination, pinching, grasping, etc.
-
Gross motor skills such as jumping, running, hopping, climbing, balancing, etc.
-
-
Equipment includes the sensory boards, balance beams, climbing frame, hula hoops, etc.











Loose Parts (素材物料)
-
Loose parts are materials that can be moved, carried, combined, redesigned, lined up, and taken apart and put them back together in multiple ways.
-
Children using loose parts lead to explorations that occur naturally and learn about things.
-
Materials can be recycling, natural.










References
- Smilansky, S., & Shefatya, L. (1990). Facilitating play: A medium for promoting cognitive, socio-emotional, and academic development in young children. Psychosocial & Educational.